Bridging is the process of merging two LAN segments. Bridges function at the Data Link Layer and use 'ports' to connect to LAN segments.
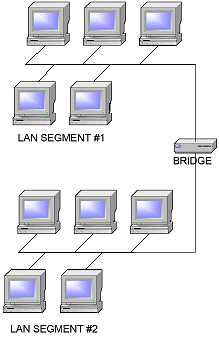
Bridging is useful when you need to:
- Maintain a flat topology.
- Reduce traffic travelling between segments, or reduce the number of hosts on a segment.
- Extend the cable length of a particular LAN segment.
- Forward Frames based on MAC address only.
BASIC BRIDGING FUNCTIONS
Learning
Bridges 'learn' the MAC address of all nodes on segments attached bridge ports by listening to traffic on each segment. The bridge stores everything it has learned in a cache table. This cache table is a list of associations between MAC addresses and the bridge ports. This table allows the bridge to associate the MAC addresses it is hearing with specific bridge port attached to the segment the node with the MAC address is on.
Forwarding
Bridges forward frames from one segment to another segment. Frames are forwarded out a specific port when the destination is known. A bridge will take a different action if the destination is unknown to it. Which action a bridge takes depends on which type of bridge it is.
Filtering
Frames are filtered in two ways:
- A received frame will never be forwarded out a port it was received on.
- Any frame that is destined for a node whose MAC address is known, and for which both the source and destination nodes are on the same segment will be filtered.
Loop Avoidance
Having two bridges connecting the same two segments creates a problem. Without special configuration, a broadcast storm can occur which eventually soaks up all the available bandwidth on both segments. Broadcast storms effectively overload the LAN with broadcast traffic thereby preventing any other hosts from transmitting.
Bridging loops are prevented by using the Spanning Tree algorithm. Bridges running Spanning Tree will shut down certain ports to certain segments and allow the root bridge to perform forwarding between the segments. This prevents bridges from forwarding other bridges broadcasts, and thereby triggering a broadcast storm.