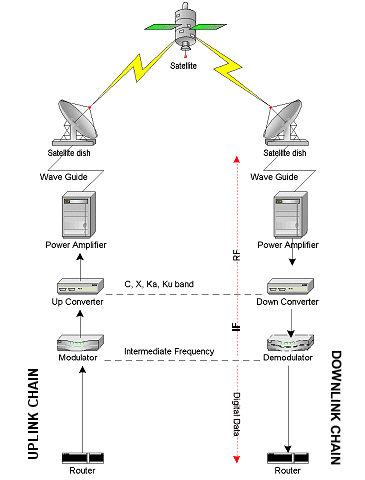
The term uplink chain is used to refer to the series of pieces of equipment that are used to produce a radio frequency signal for sending out data. The description provided here is imprecise as the exact configuration can vary widely. The downlink chain is built using nearly the same equipment in reverse order.
Take a look at the drawing below and note the path of devices on the left hand side with all the up arrows.
 DIGITAL
SATELLITE UPLINK CHAIN
DIGITAL
SATELLITE UPLINK CHAIN
How it works:
- Digital data is sent to the modulator which takes the data and converts it into a modulated signal in the Intermediate Frequency range (70-140 Mhz). The modulators use standards such as Digital Video Broadcast to organize communication over the microwave link.
- The Intermediate Frequency is piped to an "up converter" (usually via shielded coaxial cable) which mixes the intermediate frequency with a higher frequency to produce a final frequency which carries the modulated data.
- Noise is removed from the signal via either a band pass filter or other means and then it is amplified in a Klystron, Travelling Wave Tube or Solid State amplifier.
- The final cleaned signal is transmitted down the wave guide to the dish.
- The feed horn at the focal point of the dish emits the high frequency radio transmission, which the dish focuses into a directional transmission at the satellite.
Computer data is sent through a serial cable to a modulator. The modulator takes the data and produces a radio freqency from it. This frequency is usually in what is called the 'L-band' range (70-140Mhz). The modulator passes the information over coaxial cable to an 'up converter', which converts the radio frequency from 'L-band' up to microwave freqencies in the C, S, X, Ka, and Ku band ranges (frequencies above 1,000 Mhz). Once the final signal has been produced, it's amplified to increase its total effective output power. The signal is then sent out a dish via the feed horn.
DOWNLINK CHAIN
How it works:
- The satellite transmits a signal containing data
- The signal is received at the sattellite dish
- The signal is amplified and fed to the Down Converter
- The Down Converter downmixes the signal to create an intermediate frequency
- The intermediate frequency is fed to the demodulator and converted into a data signal
- The datastream is forwarded into the network via a router.